Assessing the Influence of Economic Policies and Mechanisms on Quality of Life in Kyrgyzstan: A Comprehensive Analysis
Оценка влияния экономической политики и механизмов на качество жизни в Кыргызстане: комплексный анализ
In recent years, Kyrgyzstan has experienced notable shifts in its economic landscape, driven by various policy reforms and mechanisms aimed at fostering sustainable growth and social development. As a landlocked country with a transitioning economy, Kyrgyzstan faces the complex challenge of balancing economic expansion with the enhancement of residents’ quality of life, which encompasses health, education, employment, and subjective well-being. The period from 2019 to 2023 has been particularly pivotal, marked by efforts to stimulate GDP growth, improve income distribution, and promote social equity through targeted public policies and reforms. Despite observable economic progress, questions remain about how these macroeconomic indicators translate into tangible improvements in everyday living standards for the population. Specifically, understanding the influence of economic policies—such as employment initiatives and social equity programs—on key quality of life components is essential for evaluating their effectiveness and guiding future development strategies. This research aims to explore the intricate relationship between economic factors and societal well-being in Kyrgyzstan by examining how GDP growth, employment rates, income distribution, and social initiatives impact health, education, and overall happiness of residents. Employing a comprehensive methodology that integrates quantitative secondary data analysis with qualitative case studies, the study reveals that while recent economic growth has generally contributed to improved living standards, the realization of equitable and sustainable development depends heavily on effective job creation, social inclusion, and the enhancement of public services. Ultimately, this paper seeks to provide a nuanced understanding of how economic policies and mechanisms shape the quality of life in Kyrgyzstan, offering valuable insights for policymakers aiming to foster inclusive growth and societal progress.
Impact of economic policies and mechanism on quality of life in Kyrgyzstan is a statement concerned with a viable question: “How do GDP growth and income distribution affect health, education, and well-being indicators in Kyrgyzstan?” The interplay between GDP growth and income distribution profoundly shapes health, education, and overall well-being in Kyrgyzstan, revealing a complex web of interconnections across these domains. While periods of economic growth have brought improvements in aggregate indicators, the benefits are not evenly distributed, with pronounced disparities persisting between urban centers like Bishkek and more remote regions, ultimately affecting access to healthcare and quality education [1]. Educational attainment, often heralded as a pathway to greater well-being, remains unevenly distributed, with gender and regional inequalities constraining opportunities for certain groups, particularly rural girls who face unique barriers to educational advancement [2]. Income inequality compounds these disparities: those with higher education tend to achieve greater subjective well-being and health outcomes, while individuals in lower-income brackets, often residing outside major urban centers, experience limited access to essential services and lower life satisfaction [3]. This stratification undermines the potential for broad-based human development, as improvements in GDP alone are insufficient if not coupled with targeted interventions to reduce inequalities and ensure equitable access to health and education resources. Thus, effective policy action is urgently needed to bridge these divides, promote inclusive growth, and foster a more equitable distribution of well-being across the population.
In more depth about the role of employment rates and job creation in shaping residents’ quality of life between 2019 and 2023, it is essential to indicate the employment rates and job creation parameters in the recent retrospective, given the following:
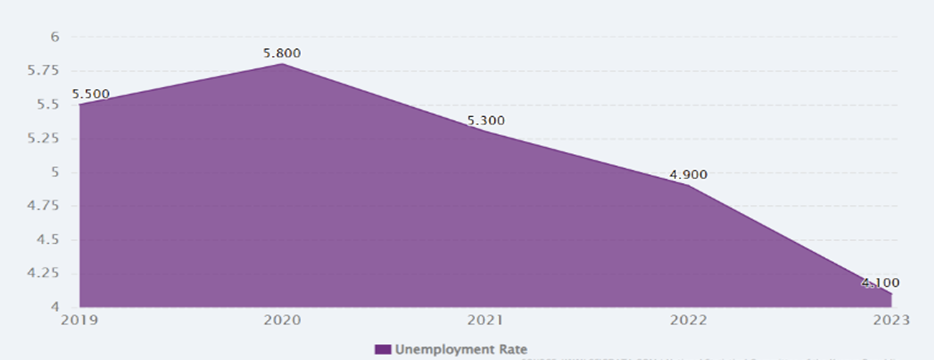
Employment rates and job creation between 2019 and 2023 have emerged as pivotal determinants in shaping residents’ quality of life, influencing domains such as economic stability, social cohesion, and individual well-being. As employment opportunities expanded, particularly in regions experiencing robust economic growth, residents reported higher levels of life satisfaction, which can be attributed to increased financial security and improved access to essential services [4].
Figure 1. Kyrgyzstan’s unemployment rate from 2019 to 2023 [9]
This interconnection is evident in studies that highlight the role of job creation not only in reducing unemployment but also in fostering urban competitiveness and attracting further investment, thereby establishing a virtuous cycle that benefits the broader community [5]. Furthermore, the direct and indirect effects of employment—such as enhanced social integration, reduced poverty, and strengthened family resilience—underscore the importance of targeted government policies that prioritize sustainable job growth and equitable access to employment opportunities [6][7]. Given these multifaceted impacts, it is imperative for policymakers to continually monitor labor market trends and implement interventions that ensure inclusive job creation, thereby safeguarding and enhancing residents’ quality of life in the face of evolving economic landscapes. Crucial to note the ways for social equity initiatives and improvements in public services influencing living standards.
Social equity initiatives and improvements in public services are deeply interconnected, collectively shaping overall living standards by addressing disparities in access to essential resources, particularly for marginalized populations. For instance, targeted subsidies in countries such as Colombia and Chile have been strategically implemented to direct resources toward underserved areas, reflecting a focused approach to narrowing the urban-rural divide in public services and thus reducing poverty and promoting equity [8].
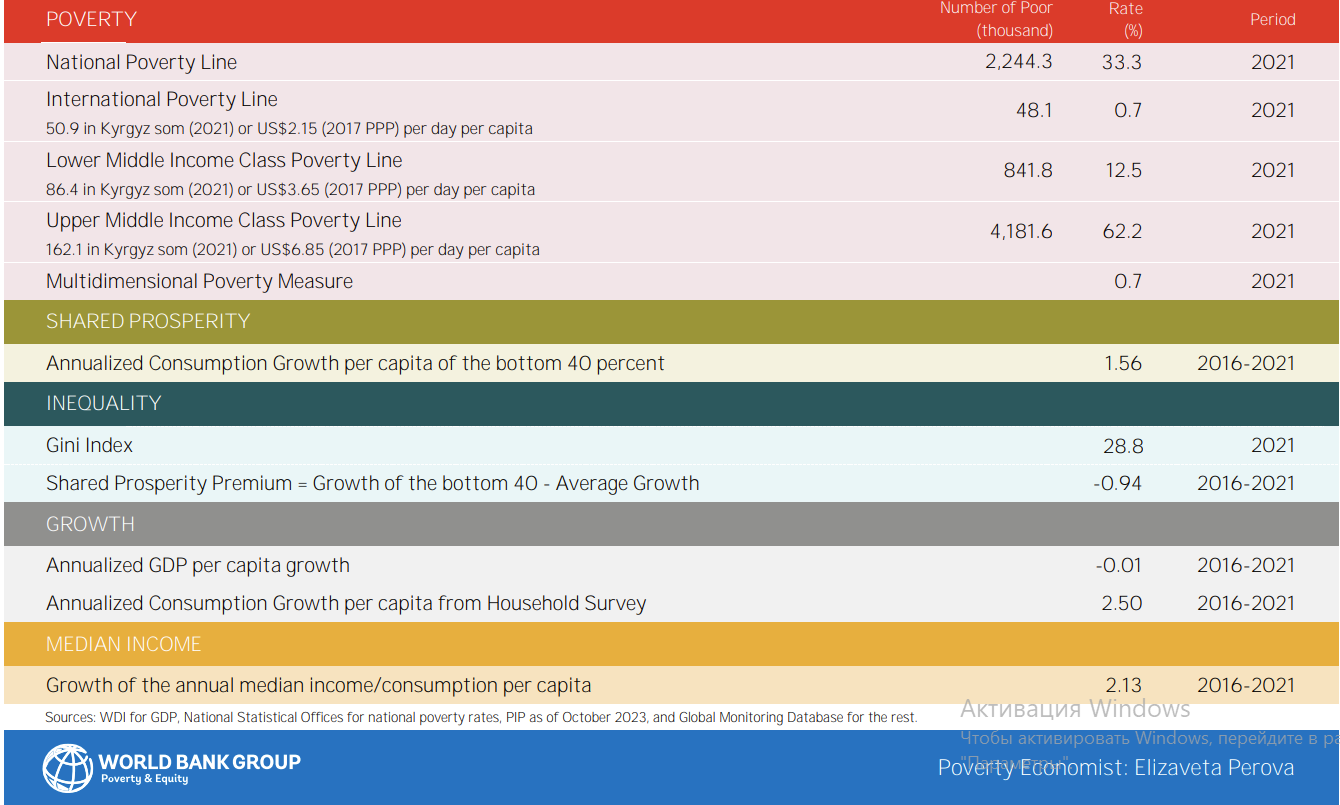
Table 1
Poverty and equity brief 2024 [10]
These targeted interventions show the critical role of state policies and public funding in bridging service gaps, especially for populations living in unfavorable conditions, where direct market mechanisms often fail to deliver equitable outcomes [8]. However, the effectiveness of such initiatives hinges on the presence of robust institutional frameworks, transparent procedures, and high administrative efficiency to ensure that subsidies genuinely reach those in need, rather than inadvertently benefiting wealthier sectors and undermining social efficiency [8]. Furthermore, enhancing access to basic services such as water supply and sanitation not only improves public health and reduces the burden on caregivers but also indirectly fosters social mobility—evidenced by higher education rates, particularly among girls, when water accessibility is improved [8]. As these domains interact, it becomes clear that a holistic, long-term approach—incorporating community participation, technological adaptation, and rigorous policy evaluation—is essential to sustain progress and ensure that social equity initiatives translate into tangible improvements in living standards [8]. In sum, to meaningfully elevate overall well-being, policymakers must prioritize inclusive frameworks and sustained investment in public services, while continually assessing outcomes to guarantee that equity are achieved.
The findings of this study underscore the critical role that economic policies and mechanisms play in shaping the quality of life in Kyrgyzstan, aligning with existing literature that emphasizes the importance of equitable economic development for sustainable human well-being. The observed disparities in income distribution, particularly between urban and rural areas and across genders, highlight persistent challenges in achieving social equity, which are consistent with previous research indicating that uneven economic gains can hinder overall social cohesion and inclusive growth. The emphasis on employment rates and job creation from 2019 to 2023 demonstrates that economic stability is closely linked to improved life satisfaction and social cohesion, suggesting that targeted policy interventions in these areas could yield significant benefits. However, the study also reveals notable limitations, such as potential data constraints or regional variations that may not be fully captured, which could influence the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, while the analysis advocates comprehensive policy measures—such as social equity initiatives and infrastructure improvements, future research should explore the specific mechanisms through which these policies impact different demographic groups, including marginalized populations. Moreover, longitudinal studies could provide deeper insights into the long-term effects of policy changes on quality of life. Recognizing potential availability as regional disparities and data availability, is essential for interpreting the results accurately. Overall, this research contributes valuable knowledge to the discourse on equitable development, but further investigation is needed to refine policy strategies and ensure they effectively address the nuanced needs of Kyrgyzstan’s diverse population.
Библиографический список
1. Atamanov, A. Regional welfare disparities in the Kyrgyz Republic. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от documents1.worldbank.org2. Hunner-Kreisel, C. Foundations of well-being in children's and youth's everyday lives in Azerbaijan and Kyrgyzstan. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12187-022-09933-5
3. Esenaliev, D., Furguson, N. The Impact of Job Quality on Wellbeing: Evidence from Wageworkers and the Self-Employed in Kyrgyzstan. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3807847
4. Salmani, Y., Ariannezhad, A., Madraki, G. Unraveling the dynamics of urban desirability: a multi-faceted analysis of large cities. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s44282-023-00026-4
5. Brodny, J., Tutak, M., Bindzár, P. Measuring and assessing the level of living conditions and quality of life in smart sustainable cities in poland—Framework for evaluation based on MCDM …. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от www.mdpi.com/2624-6511/7/3/52
6. Oliveira, C., Saldanha, E., Muni, J. Examining the Interplay of Government Policy, Social Security and Quality of Life: A Study of Public Officers in Timor-Leste. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от tljbm.org/jurnal/index.php/tljbm/article/view/136
7. Hartley, K. Public perceptions about smart cities: Governance and quality-of-life in Hong Kong. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11205-023-03087-9
8. Peña, H. tec_15_e. (n.d.) получен September 17, 2025, от http://fp7.cawater-info.net/bk/iwrm/pdf/tec_15_e.pdf
9. Kyrgyzstan unemployment rate. Global Economic Data, Indicators, Charts & Forecasts. (n.d.). https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/kyrgyzstan/unemployment-rate