Ecological and economic conditions of increasing efficiency of production
Until a certain point, production could develop without taking into account its impact on the environment, because with its small scale, nature in most cases acted as a universal chemical reactor, averaging waste and processing it into substances involved in various natural processes. And only now, when the scale of artificial «metabolism» has become commensurate with their circulation in nature, and among the production wastes there were products that could not be assimilated (plastics, plastics, etc.), production came into conflict with the natural environment.
The effectiveness of any production means its effectiveness, as, the ratio between the results achieved in the process, production, and the costs that have provided them. Considering the effectiveness of economic activity in the field of nature management, it is important to clarify the essence of the environmental and economic effect as an economic or social effect, or both. The ecological and economic effect is revealed, most fully from the position of satisfying the ecological and resource needs of society, the growth of the social use value of nature.
It is possible to speak of ecological and economic efficiency only as a terminological version of the economic productivity of production, taking into account the ecological consequences of its development, where the criterion is the maximization of the ecological effect with minimal costs of nature management.
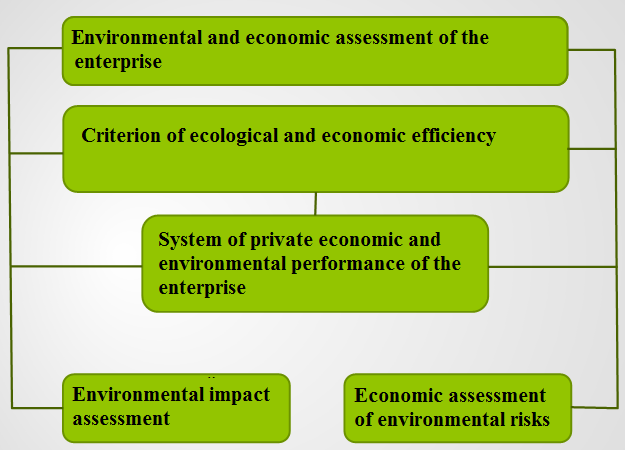
Picture 1. Scheme of environmental and economic assessment of the enterprise
Figure 1 shows the scheme of the company’s environmental and economic assessment.
In an ecological sense, the enterprises can be divided into three conventional groups: nature-regenerating, nature-oxidizing and nature-polluting. The determining environmental function for the environmental group of enterprises is the restoration, multiplication and protection of biological resources, the growth of the ecological potential of society.
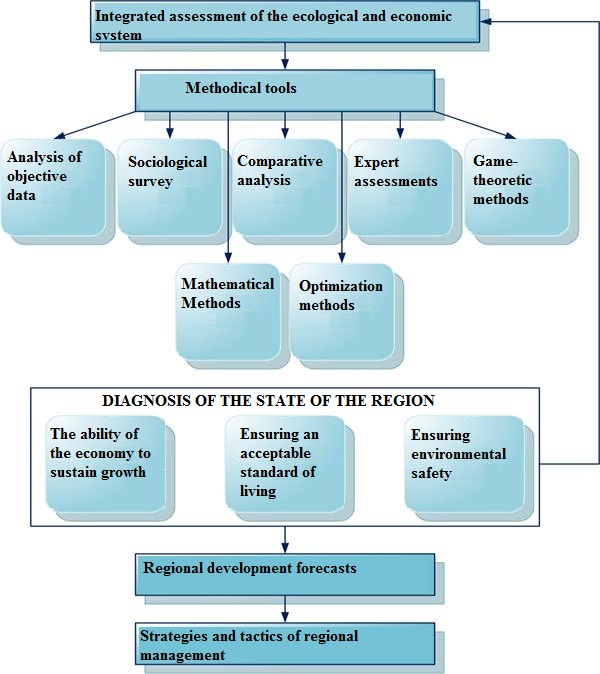
We can see at scheme of integrated assessment of the ecological and economic system at picture 2.
Picture 2. Scheme of integrated assessment of the ecological and economic system
Increasing the level of environmental efficiency of the enterprise can be ensured by effective management of those elements of the enterprise that have the most significant impact on the environment. Estimation of environmental efficiency is an internal process and management tool designed to provide management with information on how the organization’s environmental performance meets the specified criteria.
Estimation of environmental efficiency is a permanent process of information collection and assessment with a view to providing a current assessment of environmental performance and trends over time, allowing by comparison to assess the dynamics of the organization’s environmental performance with the criteria for this effectiveness, and: to identify the environmental aspects of the enterprise;
To assess which of them are the most important for him; set criteria for environmental efficiency; assess the compliance of environmental performance with these criteria.
The end result of absolutely ecologized production is the production of waste-free production, and the general expression of the environmental assessment of social production is the value expression of the products of non-waste production. Pollution of the environment by industrial emissions in the economic plan is simultaneously a process of specific «consumption» of elements of the environment — air, water, soil. Polluting the nature of any waste, we thereby increase the human costs of production, depreciate production, worsen the existence of society. Hence material production as it contradicts itself, because, in the final analysis, the public good decreases. If the produced material good reduces the value of the existing natural good (pure air, water, etc.) in such a size that the total amount of goods decreases, then this is a process of not expanded but narrowed production.
«The process of changing natural complexes under the influence of man’s productive activity under modern conditions is an exponentially increasing migration of elements of the territorial distribution of foci of fundamentally new compounds that are not perceived by the natural environment and do not fit into the general cycle of substances in nature. Such a process of radical restructuring of the biosphere turns into a low-management, environmentally-negative environmental factor that negatively affects natural formations and belongs to the category of environmentally dangerous structures. «[1]
The efficiency of economic activity is reduced due to environmental pollution. Damage from environmental pollution is taken into account with the help of a number of indicators: nature, general economic effect, environmental and economic efficiency, etc. Based on the concept of the ecological and economic system, any damage to the natural environment inevitably leads to damage to the economic and socio-economic subsystems.
In terms of its content, economic losses from environmental pollution are an ecological component of socially necessary costs, i.e. costs of society, caused by a negative impact on nature, including components of production and consumption of products. Currently, between the concepts of «eco-economic» efficiency of the enterprise and the «competitiveness» of the enterprise, it is possible to put an equals sign if the enterprise, being able to comply with environmental norms and restrictions, is able to function efficiently from the economic point of view.
As the growth in the cost of an enterprise, taking into account the environmental factor, plays a key role in the implementation of environmental and economic policy, special attention must be paid to the methodology for calculating this cost, the scientific basis of which determines the level of reliability of the results obtained, and, consequently, the adoption of managerial decisions.
Ecological and economic policy is implemented through a special system of tools and methods:
1) Ecological and economic analysis and environmental and economic assessment of the economic activity of the enterprise;
2) The system of production and environmental management;
3) The system of ecological and economic growth of the enterprise’s capital;
4) System of competitive eco-oriented production.
One of the most important instruments for implementing the company’s environmental and economic policy, along with a built-up system of motivational resource saving relationships, is compulsory environmental insurance, based on the economic assessment of environmental risks, which are the likelihood of harm to the environment and related human activities «Innovative processes of ecological orientation are based on technological and organizational innovations, which represent the beginning of a radical transformation and restructuring of the industry under the impact of environmental requirements. Products of innovative activity, characterized by improved or unique properties in an environmental sense, can become highly competitive in the market and bring, respectively, a significant income»[2].
The economic mechanism of rational nature management must be built into the economic system of society, rather than solving separately individual environmental problems. Such a mechanism should be market-oriented, with the regulatory role of the state, whose functions include determining the main directions, parameters and order of its application.
A more thorough study of the environmental factor will most likely lead to an increase in the company’s costs of environmental activities, which will affect the new selling price of commodity products: however, a comprehensive inventory of all components of the effectiveness indicators of environmental management mechanisms will help to choose the right economic solutions for a long period of time.[3]
The transition to environmentally friendly production requires a simultaneous solution of economic, technical, organizational and environmental problems. In this aspect, the problem of assessing the environmental and economic efficiency of production is updated in the formulation of the problem of accounting for the effectiveness of the growth factor in the evaluation of the value of the created assets (future economic benefits) and the environmental factor.
The condition of full compensation of environmental losses in the field of nature-exploiting activities and economic losses in the sphere of protection and reproduction of natural resources and benign environmental conditions is one of the important methodological prerequisites for assessing the results of social production.
[1] МОДЕРНИЗАЦИЯ ЭКОЛОГО-ЭКОНОМИЧЕСКОГО МЕХАНИЗМА УПРАВЛЕНИЯ РЕГИОНАЛЬНЫМИ ЗЕМЕЛЬНЫМИ РЕСУРСАМИ. Шер М.Л., Ковалева О.В., Миронов Л.В. Региональная экономика. Юг России. 2015. № 3 (9). С. 49-63.
[2] МОДЕРНИЗАЦИЯ ЭКОЛОГО-ЭКОНОМИЧЕСКОГО МЕХАНИЗМА УПРАВЛЕНИЯ РЕГИОНАЛЬНЫМИ ЗЕМЕЛЬНЫМИ РЕСУРСАМИ. Шер М.Л., Ковалева О.В., Миронов Л.В. Региональная экономика. Юг России. 2015. № 3 (9). С. 49-63.
[3] КОМПЛЕКСНОСТЬ ПОКАЗАТЕЛЕЙ ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТИ МЕХАНИЗМОВ ПРИРОДОПОЛЬЗОВАНИЯ Шер М.Л., Ковалева О.В., Миронов Л.В. Aspectus. 2014. № 4. С. 110-114.
Библиографический список
1. ИНСТИТУЦИОНАЛЬНЫЕ ОСНОВЫ ОРГАНИЗАЦИИ РЫНКА ПОСРЕДНИЧЕСКИХ УСЛУГ В СФЕРЕ ВЫСОКОТЕХНОЛОГИЧНЫХ ПРОДУКТОВ В РОССИИ. Марина Леонидовна Шер. М. Л. Шер. Краснодар, 2011.2. КОМПЛЕКСНОСТЬ ПОКАЗАТЕЛЕЙ ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТИ МЕХАНИЗМОВ ПРИРОДОПОЛЬЗОВАНИЯ Шер М.Л., Ковалева О.В., Миронов Л.В. Aspectus. 2014. № 4. С. 110-114.
3. МОДЕРНИЗАЦИЯ ЭКОЛОГО-ЭКОНОМИЧЕСКОГО МЕХАНИЗМА УПРАВЛЕНИЯ РЕГИОНАЛЬНЫМИ ЗЕМЕЛЬНЫМИ РЕСУРСАМИ. Шер М.Л., Ковалева О.В., Миронов Л.В. Региональная экономика. Юг России. 2015. № 3 (9). С. 49-63.
4. ПЕРСПЕКТИВЫ РАЗВИТИЯ РЫНКА ПОСРЕДНИЧЕСКИХ УСЛУГ В СФЕРЕ ВЫСОКОТЕХНОЛОГИЧНЫХ ПРОДУКТОВ. Шер М.Л. Экономика и предпринимательство. 2012. № 6 (29). С. 35-39.
5. Hauksworth, D. Biodiversity and conservation in Europe / D. Hauksworth, F. Bull. – Berlin : Springer-Verlag, 2012. – 201 p.